Custom Antenna for Drone and UAV Systems
Precision antenna solutions for drones and UAVs: high-performance design powering GPS, telemetry, video, and next-gen aviation tech.

Design your Drone and UAV Antennas Now
An antenna engineer will contact you with a free consultation and detailed guidance.
Why Antenna Performance Defines UAV and Drone Success
In UAVs and drones, the antenna is not just another component — it’s the lifeline that connects the aircraft to the ground and its surroundings. Whether it’s delivering real-time video, maintaining control signals, or receiving GPS coordinates, antennas directly determine the reliability, range, and safety of your drone.
Drone RF and antenna systems may be complex, but the rule is simple: if the antenna fails, the drone fails.
Unlike ground-based systems, drones operate in three-dimensional, constantly shifting environments. Every flight depends on stable links for control commands, telemetry data, real-time video transmission, satellite navigation, and sometimes even cloud connectivity. If any one of those connections drops — even momentarily — the entire operation can fail. For long-range, high-speed, or autonomous drones, the stakes are even higher.
But maintaining consistent wireless performance in flight isn’t easy. UAV antennas must be compact and lightweight, yet still efficient enough to deliver strong signal strength across a variety of frequencies. They must operate in the presence of motor noise, changing orientations, carbon fiber structures, and challenging atmospheric conditions — all without compromising range or latency.
That’s why antenna performance defines the success of every UAV. It affects how far the drone can fly, how clear the video feed remains, how precise the GPS signal is, and how reliably it can return home. Without a well-engineered antenna, even the most advanced flight controller or sensor suite becomes unreliable. Because of the significant role of the antenna in drone and UAV performance, it is highly recommended to avoid using off-the-shelf antennas. The best approach is to order your drone and UAV antennas to be custom designed based on your specific requirements. Wavelength 360 is the best online antenna design platform, where certified antenna engineers design drone and UAV antennas.

Challenges in Antenna Design for Drones and UAVs
Designing antennas for drones and UAVs comes with a unique set of challenges that differ significantly from other wireless systems. In airborne applications, antennas must deliver exceptional performance under strict constraints for weight, space, orientation, interference, and environmental reliability. A minor compromise in design can lead to major performance issues — and in UAVs, that often means loss of signal, data, or control.
Here are the key challenges engineers and manufacturers face when integrating antennas into UAV platforms:
1. Limited Space and Weight Constraints
Every gram matters in a flying system. UAV designers are constantly balancing payload capacity, battery life, and aerodynamic shape — leaving minimal space for antennas. The challenge is to integrate lightweight, low-profile antennas without sacrificing gain or efficiency. External whips may offer better range, but they add drag and mass, while internal antennas risk detuning from nearby components.
2. Changing Orientation and Radiation Patterns
Unlike fixed devices, drones constantly change direction and pitch during flight. This affects how the antenna radiates and receives signals, especially for directional systems like video downlinks or GPS. Maintaining reliable performance regardless of heading or attitude requires broad radiation coverage and careful placement.
3. Structural Interference and Material Detuning
Carbon fiber, commonly used in UAV frames, is a conductive material that can significantly detune or block antennas. Placing antennas near metal fasteners, ESCs, batteries, or motor arms often leads to degraded signal strength. Designers must account for this in simulation and consider non-traditional antenna locations to maintain performance.
4. Electromagnetic Noise from Motors and Electronics
Brushless motors, ESCs, and switching power supplies generate high levels of EMI (electromagnetic interference) that can affect sensitive antenna systems — especially on telemetry or GPS bands. Proper shielding, filtering, and antenna isolation are essential to prevent signal degradation and maintain clean data streams.
5. Long-Range, Low-Latency Requirements
UAVs often operate over long distances with minimal tolerance for latency. This demands efficient antennas with optimal impedance matching to minimize packet loss, retransmissions, or signal fade. For applications like real-time FPV or precision agriculture, the margin for error is small — and antennas must perform consistently at the edge of the coverage area.
6. Environmental and Mechanical Reliability
Antennas on UAVs are exposed to wind, vibration, temperature fluctuations, and impact forces during landings or collisions. Unlike lab conditions, the real-world environment can test every detail of the antenna’s durability. Designs must consider mechanical reinforcement, waterproofing, and tuning stability across all operational conditions.
In UAV systems, every one of these challenges converges into a high-stakes design decision. Off-the-shelf antennas may seem convenient, but rarely account for all of these variables — which is why custom antenna design is not just preferred, but often necessary.

What Type of Antenna Is Best for Drones and UAVs?
When it comes to UAVs and drones, the “best” antenna is not a single universal design — it’s the one that fits your mission profile, airframe, payload, and communication system. Whether you’re flying a lightweight quadcopter with a 5-minute flight time or a long-range fixed-wing drone conducting mapping surveys over 20 km, antenna selection must align with your flight and data requirements.
Here are the most common antenna types used in drone systems — each with their own strengths, limitations, and ideal use cases:
GNSS Patch Antennas
Used for: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou positioning
- Compact and typically mounted flat on the drone’s top surface
- Requires a stable ground plane for best accuracy
- Dual-band and multi-constellation support improves precision
💡Tip: Keep patch antennas away from motors and carbon fiber to avoid detuning.

Circularly Polarized Antennas
Used for: FPV and HD video transmission (5.8 GHz, 2.4 GHz)
- Optimized for handling orientation changes and multipath reflections
- Common in racing drones and broadcast-quality aerial video
- Typically mounted externally for maximum coverage
💡 Tip: Use matching polarization on both transmitter and receiver for consistent signal quality.
Dipole and Whip Antennas
Used for: RC control links, telemetry (433 MHz, 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz)
- Simple and efficient with omnidirectional coverage
- Flexible designs help absorb shock during landings
- External placement increases range, but adds drag
💡 Tip: Mount vertically or away from carbon surfaces to maintain radiation symmetry.
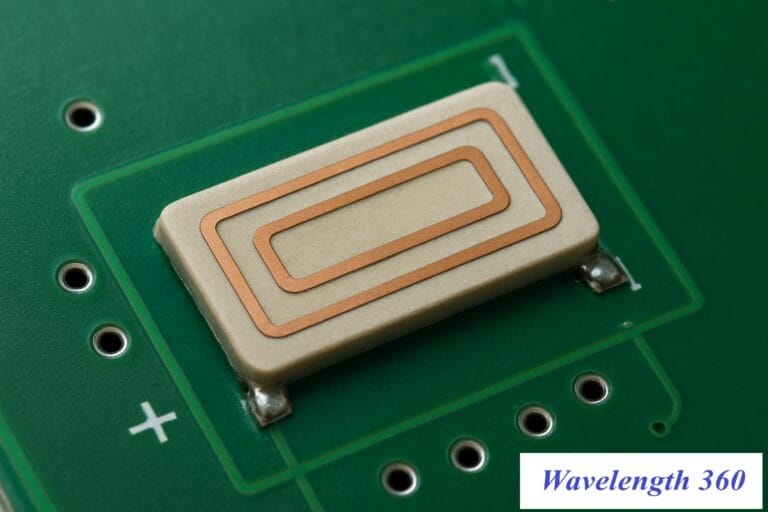
Embedded PCB or Chip Antennas
Used for: Small drones with tight space or low visual profile
- Integrated into the PCB or enclosed within the drone body
- Lightweight and low-cost, but sensitive to placement and surroundings
- Ideal for short-range or swarm applications
💡 Tip: These antennas must be matched precisely to surrounding materials to perform well.
Directional Antennas (Yagi, Patch, Helical)
Used for: Ground stations, long-range telemetry, or point-to-point video
- High gain and long range, but narrow beamwidth
- Ideal for fixed-wing BVLOS drones or automated land surveying
- Often used with auto-tracking ground antennas
💡 Tip: Combine with onboard omnidirectional antennas to maintain signal during takeoff/landing.
LTE / 5G Combo Antennas
Used for: Cloud-connected drones, BVLOS flights, real-time data uplink
- Multi-band cellular antennas embedded into payload or fuselage
- Enables autonomous operation and remote diagnostics
- Requires certification-friendly design to meet telecom standards
💡 Tip: Use antennas rated for your region’s carrier bands (Band 3, 7, 20, etc.)
So Which Antenna Is Right for Your Drone?
The answer depends on:
- Your wireless system architecture
- The flight environment (urban vs. open field)
- Payload constraints (size, weight, shape)
- Signal priority (control? video? positioning? cloud?)
- Antenna placement and interaction with nearby components
Most drones need more than one antenna, and the challenge is making them coexist without interference or signal degradation. This is where custom solutions make the biggest difference and Wavelength 360’s antenna service is essential for achieving excellent wireless communication.
Our Custom Antenna Design Capabilities for Drone/UAV
At Wavelength 360, we specialize in custom antenna solutions tailored to the unique challenges of unmanned aerial systems. Drones are not static devices — they move fast, change orientation constantly, and operate in complex RF environments. That’s why off-the-shelf antennas often fall short.
We take a systems-level approach to antenna design, considering not just the frequency and gain, but also the airframe structure, flight dynamics, EMI sources, orientation changes, and enclosure materials. Our goal is to create antennas that work seamlessly with your drone’s design, mission profile, and operational conditions.
What We Design
Our custom drone and UAV antenna capabilities include:
- High-efficiency GNSS patch antennas optimized for accuracy, ground plane constraints, and detuning resistance
- Circularly polarized antennas for robust FPV and video transmission with minimized multipath effects
- Custom dipole and whip antennas tuned for telemetry, RC control, or long-range communication, in the 433 MHz to 2.4 GHz range
- Lightweight embedded antennas (PCB, chip, or FPC) for small drones or stealth applications
- Dual-purpose combo antennas, such as LTE + GPS or RC + telemetry, with optimized isolation
- Directional antennas (e.g., patch, panel, or helical) for BVLOS applications or tracking ground stations
We carefully model each antenna for radiation performance, orientation independence, signal isolation, and flight-ready robustness.
